
We are constantly being bombarded by certain medications marketed by several companies which ensure healing of the gut. The gut is a residing place for trillions of microorganisms that particularly includes bacteria. With the onset of some harmful bacteria, the gut microflora if well nourished and balanced by beneficial bacteria eventually highlights a good gut health. As probiotics are becoming increasingly popular these days due to its superfood qualities, prebiotics quite analogous to probiotics are equally vital to maintain a good gut.
What are prebiotics:
Prebiotics are non-digestible oligosaccharides (complex carbohydrates) which selectively promotes the growth of healthy beneficial bacteria in the gut. In simple words, they are known to be the food for probiotics. The gut/intestinal microbiota ferments the prebiotics and eventually gives rise to the short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) that possess anti-inflammatory properties.
Prebiotics are grouped under two major categories called fructo-oligosaccharides (FOS) and galacto-oligosaccharides (GOS) where the former contains inulin and the latter promotes the growth of beneficial bacteria like bifidobacteria and lactobacillus. Resistant starch also comes under prebiotics.
Prebiotics as well as probiotics are known to be resistant to the acidic pH of the stomach as the stomach acid is likely to destroy them which then loses its effectiveness in producing good bacteria.
Let’s see the Effect on the gut:
As prebiotics are non-digestible, they undergo fermentation by the gut microflora in the colon in the large intestine. As the fermentation produces short-chain fatty acids (acetate, lactate, and butyrate), it promotes the growth of beneficial bacteria like Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium in the gut by feeding on them. Prebiotics function in fecal bulking and improving bowel movements that treats constipation.
This supports a reduction in the gut pH that help in decreasing inflammation and controls serum lipid and blood glucose levels. It also favors the absorption of calcium and magnesium by eliminating pathogens and reduces the risk of colon cancer.
Apart from gut-healing properties, it also benefits the GIT as well as distant site organs.
Mode of action on gut:
As healthy and beneficial bacteria forms in the intestine with the combined effect of probiotics and prebiotics, it greatly benefits the body in many ways.
- It improves the functioning of the bowel
- Defends pathogens and reduces the multiplication of harmful bacteria
- Enhances the immune system
- Improves metabolism and maintains a good satiety
- Increases absorption of minerals
- It also helps prevent constipation, and diarrhea and is effective against irritable bowel syndrome.
Here are some examples of prebiotics:
Prebiotics are primarily found in whole grains, fibrous fruits, and vegetables. Apples, bananas, berries, Oats, wheat bran, barley, cocoa, Tomatoes, asparagus, Jerusalem artichokes, chicory root, Flaxseeds, soybeans, lentils, and legumes (chickpeas, peas, and beans). Alliums like onion, garlic, leeks, and green vegetables like dandelion greens

Prebiotics also provide other nutrients
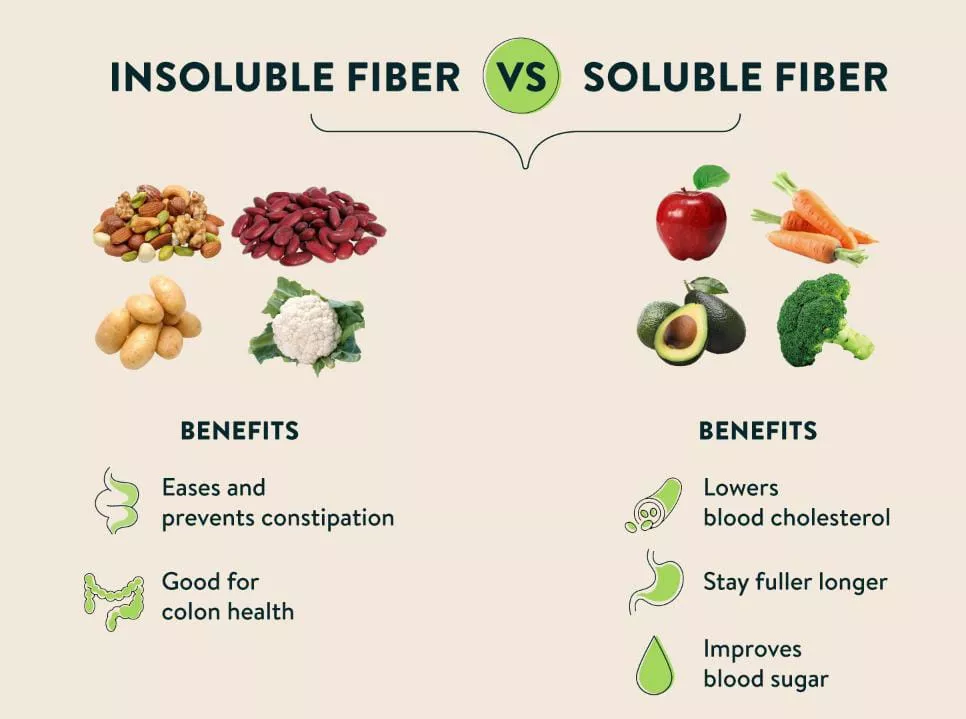
As prebiotics are highly associated with fiber, there are mainly two types of fibers classified as soluble and insoluble.
Soluble fibers are soluble in water that is easily digested by bacteria present in the small intestine. They are present in legumes and fruits. Hemicellulose (oat bran), pectin (in fruits like apples), gums, and mucilage (legumes, seaweeds, and psyllium) are the primary compounds present in soluble fibers.
Whereas insoluble fibers are those which absorb water, swell up and help in intestinal function. It is found in whole grains and vegetables.
Considering the several benefits of prebiotics, it has a huge role to play in the nourishment of gut and gut microbiota. Ideally, it is suggested to include 5 grams of prebiotics in the form of supplements. The recommended fiber intake should be 25 to 38 grams per day for adults. Also, probiotics and prebiotics should be consumed by maintaining a balance to maintain a healthy gut microbiome and gut health.

