Insulin resistance, a metabolic disorder, has emerged as a significant health concern globally, affecting millions of individuals. It is a condition wherein the body’s cells become resistant to the effects of insulin, a hormone crucial for regulating blood sugar levels. While its association with type 2 diabetes is well-known, insulin resistance also plays a pivotal role in weight management challenges and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), a common hormonal disorder among women. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve deep into understanding insulin resistance, its impact on weight loss, and how it influences the management of PCOS.
When the thyroid gland isn’t functioning optimally, it can lead to various health issues, and may cause symptoms like a puffy face, sluggishness, weight gain, difficulty losing weight, feeling cold, a slowed heart rate, constipation, depression, and thinning of hair. Fortunately, adopting specific nutrition strategies can support thyroid health and facilitate weight loss.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore effective nutrition strategies for optimizing thyroid health and achieving weight loss goals.

Understanding Insulin Resistance:
Let us first understand the role of insulin in the body. Insulin, secreted by the pancreas, helps cells absorb glucose from the bloodstream to use it as energy or store it for future use. When cells in your muscles, fat, and liver don’t respond well to insulin and can’t easily take up glucose from your blood, they become resistant to insulin and fail to respond adequately to its signals, leading to elevated blood sugar levels. To compensate, the pancreas produces more insulin, resulting in a vicious cycle of elevated insulin levels and resistance.
Causes of Insulin Resistance:
- Genetics: Genetic predisposition makes certain individuals more susceptible to developing insulin resistance.
- Obesity: Excess body weight, particularly fat around the abdomen, blocks insulin receptors and worsens the condition.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity contributes significantly to the onset of insulin resistance.
- Poor Diet: Diets high in refined carbohydrates, sugars, and saturated fats increase the risk of developing insulin resistance.
- Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions can also contribute to the development of insulin resistance.
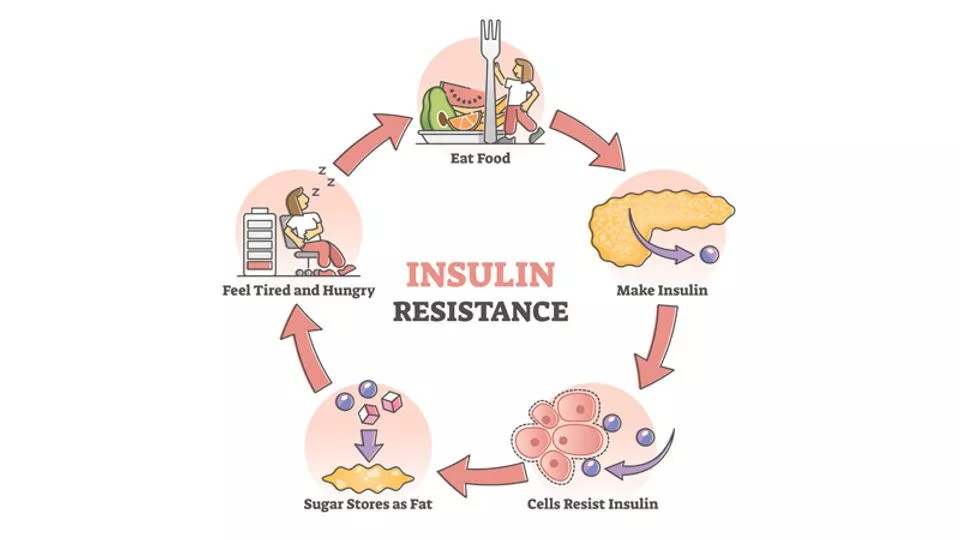
Impact on Weight Loss and PCOS:
- Challenging Environment for Weight Loss: Insulin resistance makes it difficult to lose weight because cells resist insulin's signals to absorb glucose, leading the body to store excess glucose as fat, especially around the abdomen.
- Increases Abdominal Adiposity: The accumulation of visceral fat not only worsens insulin resistance but also elevates the risk of metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular diseases.
- Hinders Fat Burning: Insulin resistance affects the body's ability to burn stored fat for energy, complicating effective weight loss.
- Leads to Hyperinsulinemia in PCOS: In PCOS, insulin resistance causes the pancreas to secrete excess insulin, leading to hyperinsulinemia.
- Elevates Androgen Levels: High insulin levels in PCOS stimulate the ovaries to produce more androgens, such as testosterone, which disrupts ovarian function and leads to symptoms like irregular menstrual cycles and infertility.
How to check yourself for Insulin Resistance:
The following are just the characteristic symptoms, however, you should consult a professional for diagnosis.
- A waistline over 40 inches in men and 35 inches in women.
- Blood pressure readings of 130/80 or higher.
- A fasting glucose level over 100 mg/dL.
- A fasting triglyceride level over 150 mg/dL.
- A HDL cholesterol level under 40 mg/dL in men and 50 mg/dL in women.
- Skin tags
- Patches of dark, pigmented velvety skin called acanthosis nigricans
Diet for Managing Insulin Resistance
Despite the challenges posed by insulin resistance, adopting certain lifestyle modifications can help manage weight effectively.
Following are some of the strategies:
Balanced Diet
Focus on a balanced diet rich in whole grains like Oats, Quinoa, and brown rice, lean proteins like legumes, eggs, and meat, healthy fats from nuts, and plenty of fruits and vegetables. Avoid processed foods, sugary beverages, and high-glycemic-index foods that spike blood sugar levels.
Regular Exercise
Engage in regular physical activity, including both aerobic exercises and strength training, for at least 30-45 min to improve insulin sensitivity, burn calories, and promote weight loss.
Portion Control
Monitor portion sizes and practice mindful eating to avoid overeating and stabilize blood sugar levels throughout the day. Plan your meals ahead with predetermined quantities.
Adequate Sleep
Prioritize adequate sleep, as insufficient sleep can disrupt hormone regulation, including insulin production and sensitivity, leading to weight gain and insulin resistance.
Stress Management
Chronic stress can exacerbate insulin resistance and hinder weight loss efforts and hormonal imbalances. Incorporate stress-reducing activities such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises into your daily routine that will help produce happy hormones.
Superfoods
Incorporating “superfoods” like Cinnamon, Apple cider Vinegar, Fenugreek seeds, Bitter gourd, Drumstick leaves, Ashwagandha, Apple cider vinegar, as well as chromium-rich foods like egg, broccoli, nuts and high-fiber foods like whole grains, leafy greens, fruits into the diet can be beneficial for managing blood sugar levels, reducing inflammation, and promoting overall health.
References
References:-
- https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/diabetes/overview/what-is-diabetes/prediabetes-insulin-resistance
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/317382
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5519190/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9665922/
- https://ovarianresearch.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13048-022-01091-0
- https://www.verywellhealth.com/pcos-and-insulin-resistance-2616319
- https://www.nytimes.com/2023/10/03/well/live/reverse-insulin-resistance.html
- https://diabetes.org/health-wellness/insulin-resistance
- https://www.webmd.com/diabetes/insulin-resistance-syndrome
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/317112